Your cart is currently empty!
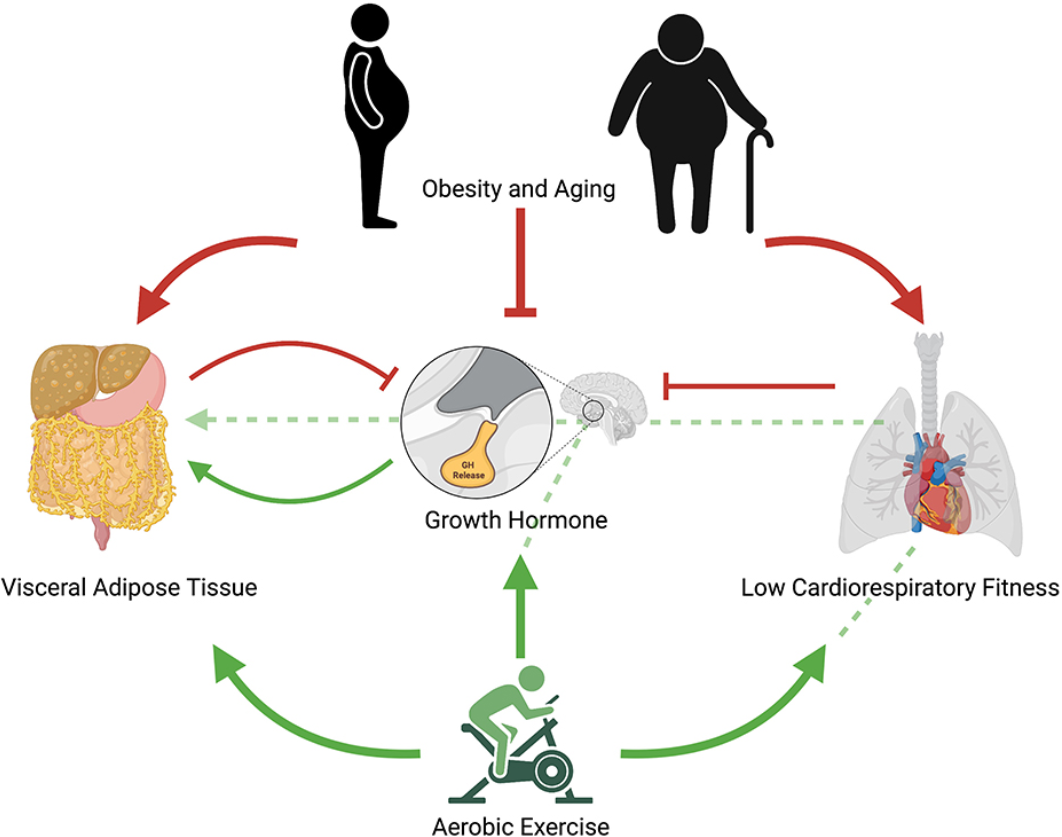
The impact of physical exercise on hormonal regulation for weight loss.
This article will take a look at physical activity from another perspective: The role of physical exercise in weight loss or weight regulation from a hormonal standpoint, or in other words – The impact of physical exercise on hormonal regulation for weight loss. Physical exercise is widely recognized as a fundamental component of weight management…

This article will take a look at physical activity from another perspective: The role of physical exercise in weight loss or weight regulation from a hormonal standpoint, or in other words – The impact of physical exercise on hormonal regulation for weight loss.
Physical exercise is widely recognized as a fundamental component of weight management strategies. Beyond its role in calorie expenditure and muscle development, exercise profoundly influences hormonal regulation, contributing to weight loss efforts. Understanding the specific types of exercise that trigger key hormones involved in weight loss is crucial for optimizing fitness routines and achieving desired outcomes.
Aerobic Exercise and Hormonal Responses: Aerobic exercise, characterized by sustained, rhythmic movements that increase heart rate and oxygen consumption, elicits significant hormonal responses conducive to weight loss. During aerobic activities such as running, cycling, or swimming, the body releases hormones such as adrenaline and noradrenaline from the adrenal glands. These hormones activate the sympathetic nervous system, leading to increased energy expenditure and fat mobilization.
Furthermore, aerobic exercise stimulates the secretion of hormones such as cortisol and growth hormone. Cortisol, often dubbed the “stress hormone,” plays a dual role in metabolism, promoting glucose utilization and facilitating fat breakdown. Growth hormone, on the other hand, supports muscle growth and fat metabolism, contributing to improved body composition.
Resistance Training and Hormonal Regulation: In addition to aerobic exercise, resistance training represents a potent modality for hormonal modulation and weight loss. Resistance exercises, involving the use of external resistance to strengthen muscles, exert unique hormonal effects that complement aerobic activities.
Resistance training stimulates the release of anabolic hormones such as testosterone and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1). These hormones promote muscle protein synthesis, muscle growth, and metabolic rate elevation, all of which contribute to increased calorie expenditure and enhanced fat loss.
Moreover, resistance exercises induce acute spikes in catecholamines, including adrenaline and dopamine, which facilitate fat oxidation and metabolic rate elevation post-exercise. This heightened metabolic state, often referred to as the “afterburn effect” or excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC), results in continued calorie burning long after the workout session concludes.
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) and Hormonal Responses:
In my previous posts, I’ve expressed my standpoint on HIIT, emphasizing its importance and the need for caution. Nevertheless, this exercise method is highly efficient and well-suited for advanced athletes.
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) has gained popularity as an effective strategy for weight loss due to its potent hormonal effects and time efficiency. HIIT alternates short bursts of intense exercise with brief recovery periods, challenging the body’s energy systems and eliciting robust hormonal responses.
HIIT sessions trigger significant releases of adrenaline and noradrenaline, promoting fat mobilization and metabolic rate elevation. Additionally, HIIT stimulates the production of human growth hormone (HGH), a key hormone involved in fat metabolism and lean muscle development.
Conclusion: In summary, various types of physical exercise exert distinct hormonal influences that facilitate weight loss and improve body composition. Aerobic exercise, resistance training, and HIIT each trigger hormonal responses conducive to fat loss, muscle growth, and metabolic enhancement. Incorporating a balanced exercise regimen that integrates these modalities can optimize hormonal regulation and support sustainable weight management efforts.
As individuals embark on their fitness journeys, understanding the intricate interplay between exercise and hormones empowers informed decision-making and enhances the efficacy of weight loss strategies. By harnessing the power of exercise-induced hormonal responses, individuals can achieve their weight loss goals and embark on a path to lifelong health and wellness.
So, if you’re intrigued by this topic, don’t hesitate to seek guidance from your coach or a physiologist advisor for advice.
Stay tuned.



One response to “The impact of physical exercise on hormonal regulation for weight loss.”
interesting and informative